Sidechains – Scaling Blockchains with Layer‑2 Solutions
When working with sidechains, independent blockchains that run parallel to a main chain. Also known as layer‑2 chains, they let developers move assets off the main chain, process transactions faster, and cut fees, then securely lock the results back on the original network. Sidechains enable faster transactions while preserving the security of the main chain through a two‑way peg. Another key player in the scaling arena is blockchain sharding, a method that splits a blockchain's data into smaller pieces called shards. Sharding horizontal scaling reduces the load on each node, complementing sidechains by handling state updates in parallel. A third related concept is Layer 2 scaling, solutions built on top of the base layer to increase throughput without changing its core protocol. Layer 2 includes rollups, state channels, and sidechains themselves, each offering a trade‑off between speed, security, and decentralisation. Finally, cross‑chain bridges, protocols that move assets between different blockchains tie the ecosystem together, allowing sidechains to interact with the main chain and other networks safely.
Why Sidechains Matter for Developers and Users
Sidechains give developers a sandbox to test new features without risking the main chain’s stability. For users, the result is lower transaction fees and near‑instant confirmations—think of moving a token from Ethereum to a Polygon sidechain to avoid the high gas price spikes. Because sidechains run their own consensus, they can adopt specialised validators or proof‑of‑authority models, which further speeds up block times. At the same time, the two‑way peg ensures that any asset locked on the main chain can be reclaimed, preserving trust. This relationship creates a semantic triple: "Sidechains enable faster transactions, which reduces user costs, and the two‑way peg preserves security." Another triple links sharding and sidechains: "Blockchain sharding distributes state, while sidechains handle transaction throughput, together enhancing overall scalability." When you add cross‑chain bridges into the mix, you get a third triple: "Cross‑chain bridges connect sidechains to other networks, expanding interoperability and opening new DeFi opportunities." These connections show why the sidechain ecosystem is a cornerstone of today’s blockchain scaling strategy.
In practice, sidechains have already powered popular projects. Polygon, for example, runs a network of sidechains that host millions of DeFi users, while Optimism uses an optimistic rollup that behaves like a sidechain with fraud proofs. Both showcase how sidechains can coexist with the main Ethereum chain, offering users choice and flexibility. If you’re curious about how sidechains compare to sharding, think of sharding as a way to split the data layer of a single chain, whereas sidechains are separate chains that talk to each other. This distinction helps you decide which tool fits your use case—whether you need a lightweight environment for rapid trades or a deep‑scale solution for massive data‑heavy applications. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive into sidechains, sharding, layer‑2 tech, and bridge security, giving you the practical insights you need to navigate the scaling landscape.
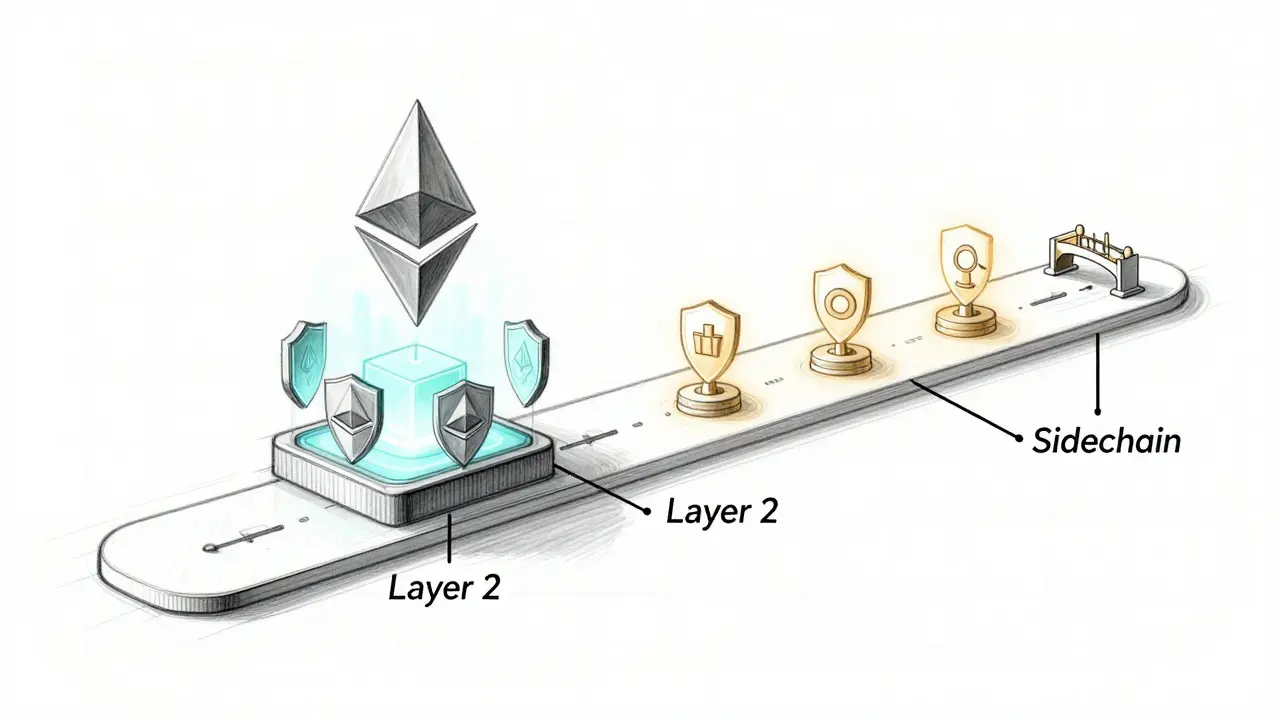
Sidechains vs Layer 2: Which Scalability Solution Fits Your Blockchain Project?
Sidechains and Layer 2 solutions both solve Ethereum's scaling issues, but they work in very different ways. Learn which one is right for your project based on security, speed, cost, and use case.
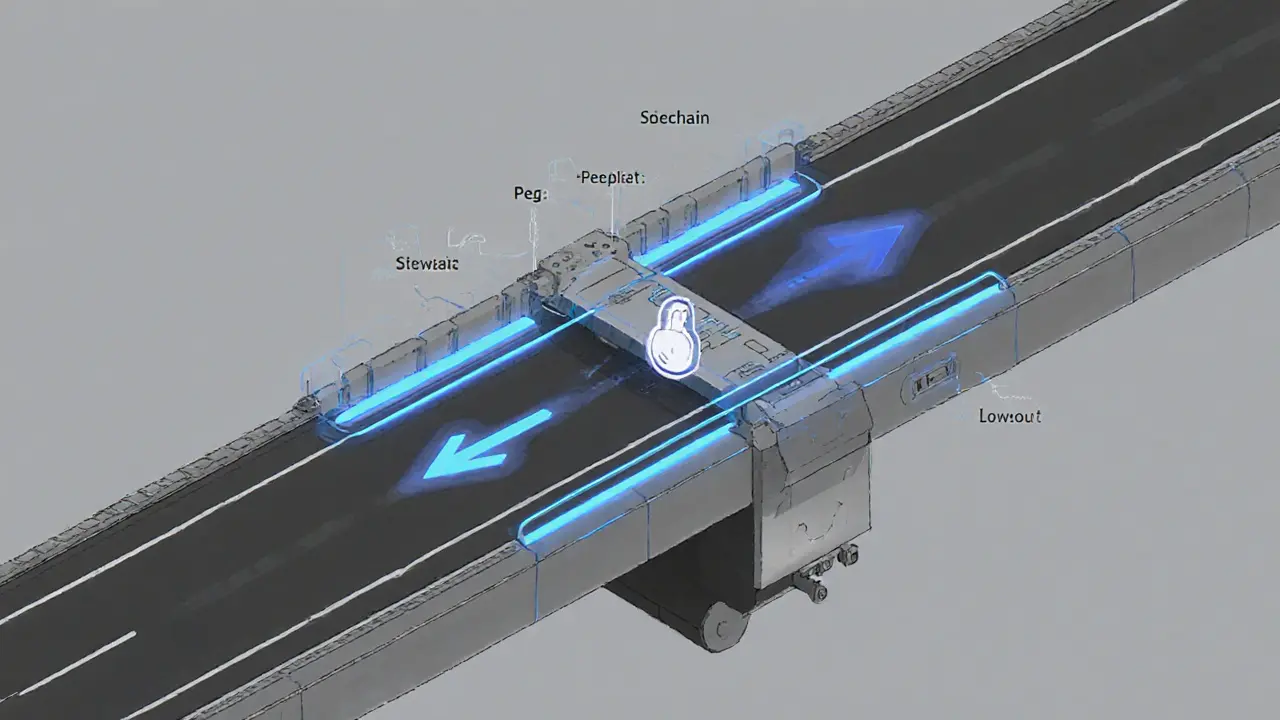
Understanding Sidechains: Scaling and Interoperability in Cryptocurrency
A clear, conversational guide explains what sidechains are, how two‑way pegs work, real‑world examples like Liquid and Rootstock, benefits, risks, and future trends.
